

This is no different from the formation of an ester between, say, ethanol and ethanoic acid - except that it is carried out under the influence of an enzyme rather than the more fierce conditions used in the lab. The amino acid gets attached to this by forming an ester link between this -OH group and the -COOH group of the amino acid. At the very end of the chain is the -OH group on the 3' carbon of a ribose ring. Remember that the bases in RNA and DNA are attached to a backbone of alternating phosphate and sugar groups. This model is quite difficult to follow, and I am going to simplify it down to pick out the two important bits of itĪt the 3' end of every transfer RNA molecule, the chain ends with the sequence of bases C C A. Most of the colour coding is irrelevant to this discussion - but note the little bit in grey at the bottom which is where the anti-codon is (see below).
A model of a typical transfer RNA looks like this: These are mostly the same bases as in messenger RNA (A, U, G and C), but it also contains some modified bases which won't concern us at this level. Transfer RNA is a short bit of RNA containing about 80 or so bases. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is responsible for carrying amino acids to the messenger RNA and then holding them there in a way that enables them to join together. The ribosome now has to build the protein chain starting with a methionine at the AUG codon it has just found.īefore we can talk about that we have to introduce transfer RNA. This pattern occurs just before the first occurrence of the AUG codon in the messenger RNA strand. It attaches to the 5' end of the messenger RNA and moves along it until it comes to a particular pattern of bases which it can bind to. The smaller bit is involved in finding the start point. Ribosomes come in two parts - a smaller bit and a larger bit. Note: If you don't know what I mean by the 5' end or by upstream, it is probably because you haven't read these pages from the beginning.
AMINO ACID SEQUENCE FROM MRNA CODE
So how does the system know where to start? How does it find the right AUG codon from all the ones which are probably strung out along the RNA to code for the amino acid methionine? There is a length of RNA upstream of the start codon which isn't actually used to build the protein chain. You may find descriptions of this process which imply (although without actually saying so directly) that the messenger RNA starts with the codon AUG - the start codon - at the 5' end. We'll take it gently and simplify it where possible.įinding the start point of the messenger RNA

The amino acids have to be carried to the messenger RNA by another type of RNA known as transfer RNA - abbreviated to tRNA (as opposed to mRNA for messenger RNA).Īll of this is controlled by a ribosome - a hugely complicated structure involving protein molecules and yet another form of RNA (ribosomal RNA or rRNA). Translating the code into an actual protein chain is complicated by the fact that individual amino acids won't interact with the messenger RNA chain.

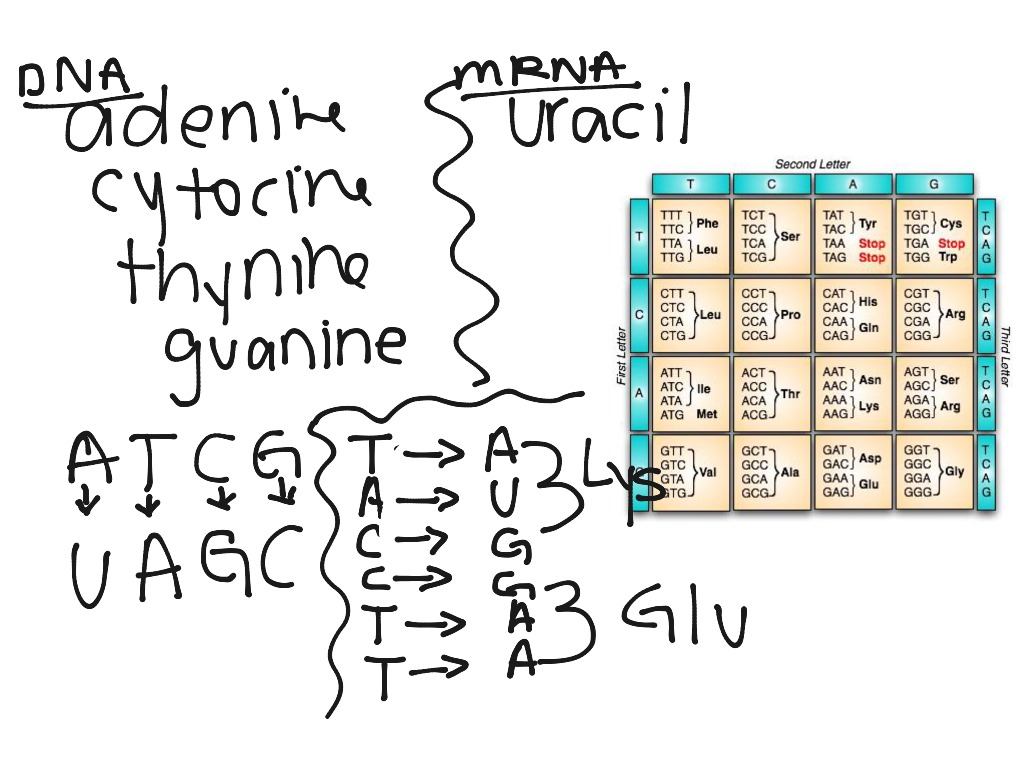
We'll look in some detail at how this works further down the page. You may also remember that three codons serve as stop codons, and one (AUG) codes for methionine, but also serves as a start codon. The table below repeats one from the previous page: Each of the sets of three bases is known as a codon. You will remember that messenger RNA contains a sequence of bases which, read three at a time, code for the amino acids used to make protein chains. It will all make more sense if you start from the beginning of the sequence with the structure of DNA. Note: If you have come straight to this page from a search engine, you should be aware that this is the fifth page in a sequence of pages about DNA and RNA. If you are a biochemistry or biology student, you will probably find it a useful introduction, but will have to look elsewhere to find all the detail you need. It is designed for 16 - 18 year old chemistry students. This page looks at how the information coded in messenger RNA is used to build protein chains.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
